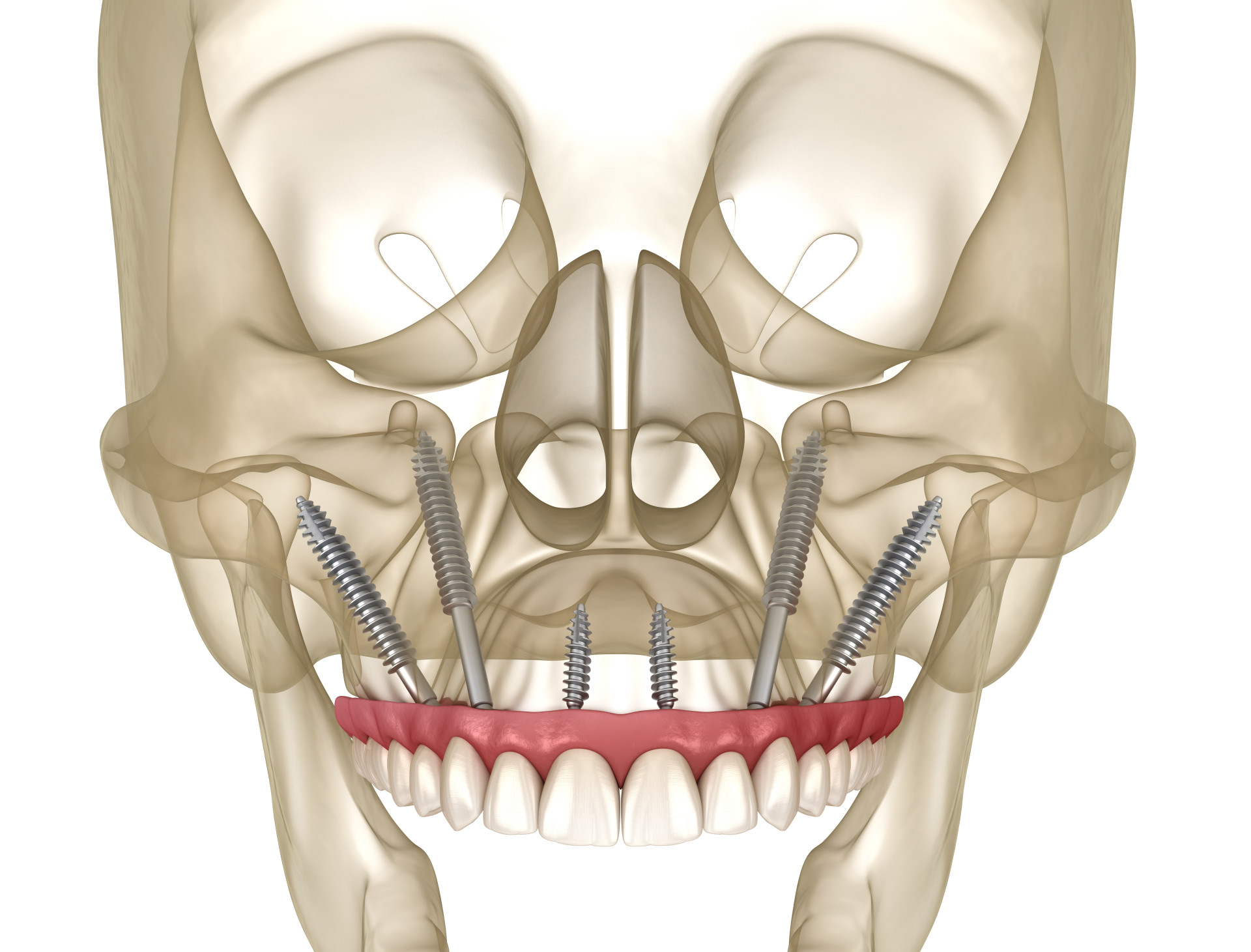
Benefits of Zygomatic Implants
One of the primary advantages of zygomatic implants is the ability to provide immediate function and esthetic results. Unlike traditional implants that may require months of healing before prosthetic placement, zygomatic implants can often support a temporary prosthesis shortly after surgery. This expedited process significantly reduces treatment time and enhances patient satisfaction.
Moreover, zygomatic implants are particularly suitable for patients who have experienced significant bone loss, either due to advanced periodontal disease, trauma, or congenital conditions. By anchoring securely into the robust zygomatic bone, these implants offer a stable foundation for dental rehabilitation without the need for complex bone augmentation procedures.
Procedure and Placement
The placement of zygomatic implants involves a surgical procedure that requires specialized training and expertise. During the surgery, the oral surgeon accesses the zygomatic bone through small incisions in the gum tissue. By anchoring the implants in the zygoma, which is denser and more stable than the maxillary bone, the surgeon can achieve secure fixation for the prosthetic teeth.
Anesthesia options vary based on patient preference and surgical complexity, with many procedures performed under local anesthesia supplemented by sedation for comfort. After the surgery, patients typically experience some swelling and discomfort, which can be managed with prescribed medications.
Candidates for Zygomatic Implants
Zygomatic implants are recommended for individuals who may not be suitable candidates for traditional dental implants due to severe bone loss in the upper jaw. Candidates often include those with:
- Severe bone resorption
- Previous failed implant procedures
- Maxillary tumors or congenital defects
Before undergoing zygomatic implant treatment, patients undergo a comprehensive evaluation to assess oral health, bone structure, and treatment goals.
Post-Procedure Care
Following zygomatic implant surgery, patients receive detailed instructions for postoperative care. This includes dietary modifications, oral hygiene practices, and recommendations for managing swelling and discomfort. Patients are advised to attend follow-up appointments to monitor healing progress and ensure optimal integration of the implants.
Potential Risks and Complications
Like any surgical procedure, zygomatic implant placement carries inherent risks, including infection, nerve injury, or implant failure. However, with proper patient selection, meticulous surgical technique, and attentive postoperative care, these risks can be minimized. Patients should be aware of potential complications and discuss any concerns with their dental team.
Success Rate and Longevity
The success of zygomatic implants depends on various factors, including patient health, surgical technique, and postoperative care. Studies have shown high success rates for zygomatic implants, with long-term outcomes comparable to traditional implant-supported restorations. Regular follow-up visits and proper oral hygiene are essential for maximizing implant longevity.